1) VNET – Overview
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) là một dịch vụ cơ bản trong Microsoft Azure, cho phép bạn tạo ra một mạng riêng ảo để kết nối và quản lý các tài nguyên như máy ảo (VM), ứng dụng, cơ sở dữ liệu, và các dịch vụ khác trong môi trường đám mây.
Các thành phần chính của VNet
- Địa chỉ IP (Address Space): Xác định phạm vi địa chỉ IP riêng cho VNet, ví dụ:
10.0.0.0/16. - Subnet: Phân chia VNet thành các phân đoạn nhỏ hơn để tổ chức và bảo mật, ví dụ:
10.0.1.0/24cho máy chủ web. - Network Interface (NIC): Kết nối giữa máy ảo và VNet, mỗi máy ảo cần ít nhất một NIC.Microsoft Learn
- Public IP: Địa chỉ IP công cộng cho phép tài nguyên trong VNet giao tiếp với internet.
- Network Security Groups (NSG): Quy tắc bảo mật để kiểm soát lưu lượng mạng vào và ra từ các tài nguyên trong VNet.
Kết nối và mở rộng VNet
- VNet Peering: Kết nối hai VNet trong cùng một hoặc khác vùng Azure, cho phép giao tiếp giữa các tài nguyên trong các VNet này.
- VPN Gateway: Kết nối VNet với mạng nội bộ của bạn qua một kết nối VPN an toàn.
- ExpressRoute: Kết nối trực tiếp và riêng biệt giữa VNet và cơ sở hạ tầng của bạn, không qua internet công cộng.
2) So sánh Azure VNet và AWS VPC
2.1) Cấu trúc và Quản lý Subnet
AWS VPC: Mỗi subnet phải được chỉ định rõ ràng vào một Availability Zone (AZ) cụ thể. Điều này giúp kiểm soát chặt chẽ vị trí và phân phối tài nguyên trong các khu vực khác nhau.
Azure VNet: Subnets không cần chỉ định AZ cụ thể; chúng có thể trải rộng trên nhiều AZ trong cùng một vùng. Điều này cung cấp tính linh hoạt cao hơn trong việc phân phối tài nguyên và tăng khả năng chịu lỗi.
2.2) Cổng Kết Nối Internet
AWS VPC: Sử dụng Internet Gateway (IGW) để cung cấp kết nối internet cho các subnet công cộng.
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/premier-developer/differentiating-between-azure-virtual-network-vnet-and-aws-virtual-private-cloud-vpc
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/bhavesh-atara-928286a_aws-vpc-vs-azure-vnet-key-differences-in-activity-7249630752370216961-e8MG
https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/startupsatmicrosoftblog/key-architectural-differences-between-aws-and-azure-explained/4244702
Azure VNet: Không cần IGW; thay vào đó, các tài nguyên có thể được gán Public IP trực tiếp hoặc sử dụng các dịch vụ như NAT Gateway để truy cập internet.
https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/startupsatmicrosoftblog/key-architectural-differences-between-aws-and-azure-explained/4244702?utm_source=chatgpt.com
2.3) Bảo Mật và Kiểm Soát Lưu Lượng
AWS VPC: Cung cấp hai lớp bảo mật: Security Groups (SGs) cho kiểm soát lưu lượng trạng thái (stateful) và Network ACLs (NACLs) cho kiểm soát lưu lượng không trạng thái (stateless). https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/startupsatmicrosoftblog/key-architectural-differences-between-aws-and-azure-explained/4244702?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Azure VNet: Sử dụng Network Security Groups (NSGs) để kiểm soát lưu lượng ở cấp độ subnet hoặc giao diện mạng, với các quy tắc trạng thái (stateful).
2.4) Kết Nối Liên Vùng và Liên Vùng
AWS VPC: Hỗ trợ VPC Peering và Transit Gateway để kết nối các VPC trong cùng hoặc khác vùng. Tuy nhiên, việc kết nối giữa các VPC ở các vùng khác nhau có thể yêu cầu cấu hình phức tạp hơn.
https://dev.to/shreya111111/cloud-networking-showdown-aws-vpc-vs-azure-vnet-vs-google-cloud-vpc-5e61?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Azure VNet: Hỗ trợ VNet Peering trong cùng một vùng hoặc giữa các vùng khác nhau, với khả năng truyền tải lưu lượng giữa các VNet mà không cần đi qua internet công cộng.
2.5) Tính Năng và Dịch Vụ Hỗ Trợ
AWS VPC: Cung cấp nhiều dịch vụ mạng như Elastic Load Balancing, AWS Direct Connect, và PrivateLink để kết nối với các dịch vụ AWS khác hoặc với mạng nội bộ.
https://dev.to/shreya111111/cloud-networking-showdown-aws-vpc-vs-azure-vnet-vs-google-cloud-vpc-5e61
https://www.techtarget.com/searchcloudcomputing/tip/Compare-Amazon-VPC-vs-Azure-VNet-for-private-networking
Azure VNet: Tích hợp chặt chẽ với các dịch vụ của Microsoft như Active Directory, SQL Database và cung cấp các tùy chọn kết nối như ExpressRoute và VPN Gateway.
3) Create a complete VNet infrastructure on Azure using Terraform.
3.1) Create Versions for the running Terraform.
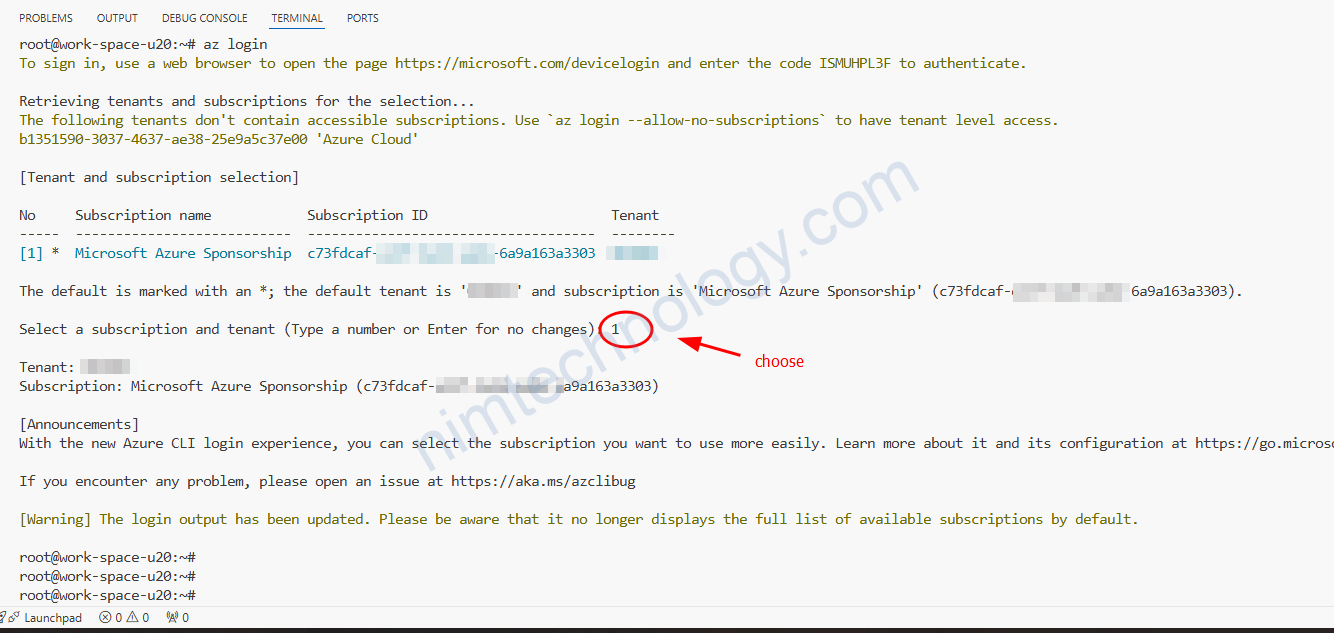
Bạn cần thực hiện azure login đẻ thấy được Subscription ID
3.2) Create a VNet on the Azure cloud.
# Create Virtual Network
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {
name = var.vnet_name
address_space = var.vnet_address_space
location = var.resource_group_location
resource_group_name = var.resource_group_name
tags = local.merged_tags
}
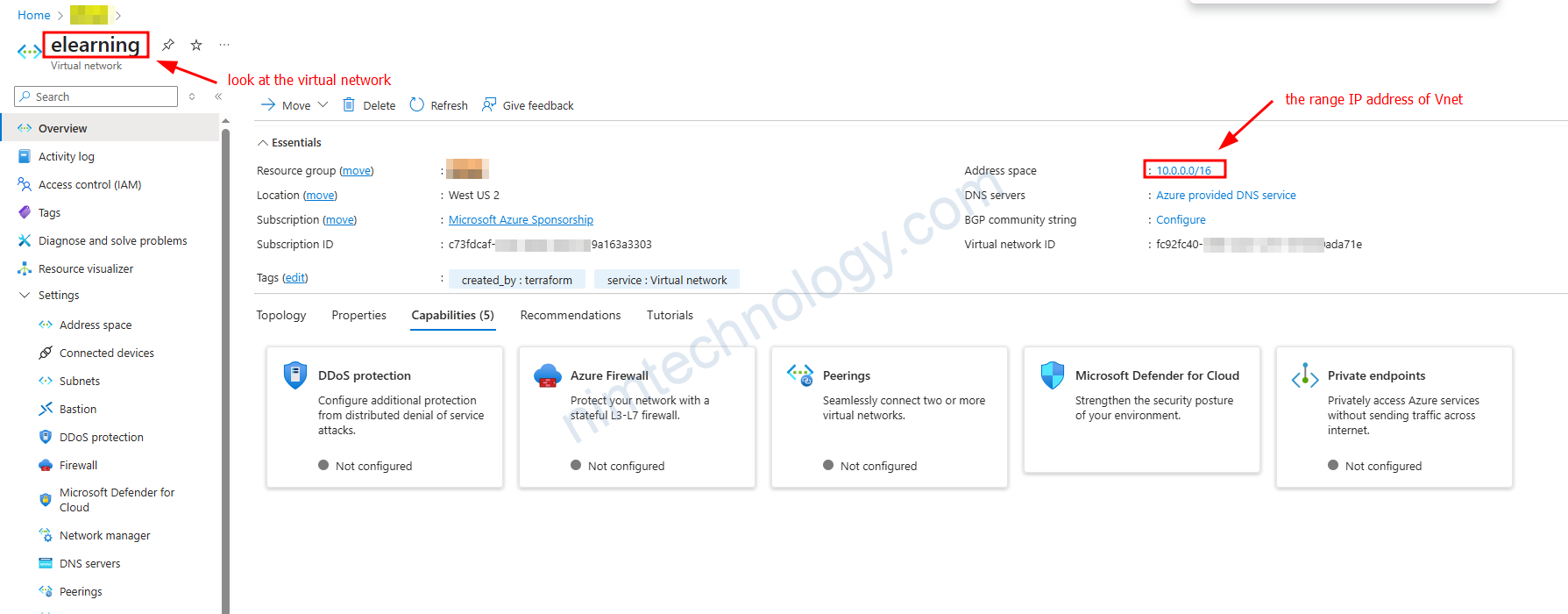
Sau khi bạn Run xong resource “azurerm_virtual_network” “vnet” thì sẽ được Virtual Network như ảnh.
3.3) Create Subnet on Azure Cloud
Tiếp tục chúng ta sẽ chia nhỏ vnet thành nhiều subnet. Vì subnet mới là phần tử được sử dụng để cung cấp cho các component.
# Resource-1: Create the Subnets
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnets" {
count = length(var.subnets)
name = "${var.vnet_name}-subnet-${count.index + 1}"
resource_group_name = var.resource_group_name
virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.name
address_prefixes = [var.subnets[count.index]]
}
resource "azurerm_subnet_nat_gateway_association" "subnet_nat_assoc" {
count = length(azurerm_subnet.subnets)
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].id
nat_gateway_id = azurerm_nat_gateway.nat_gateway.id
}
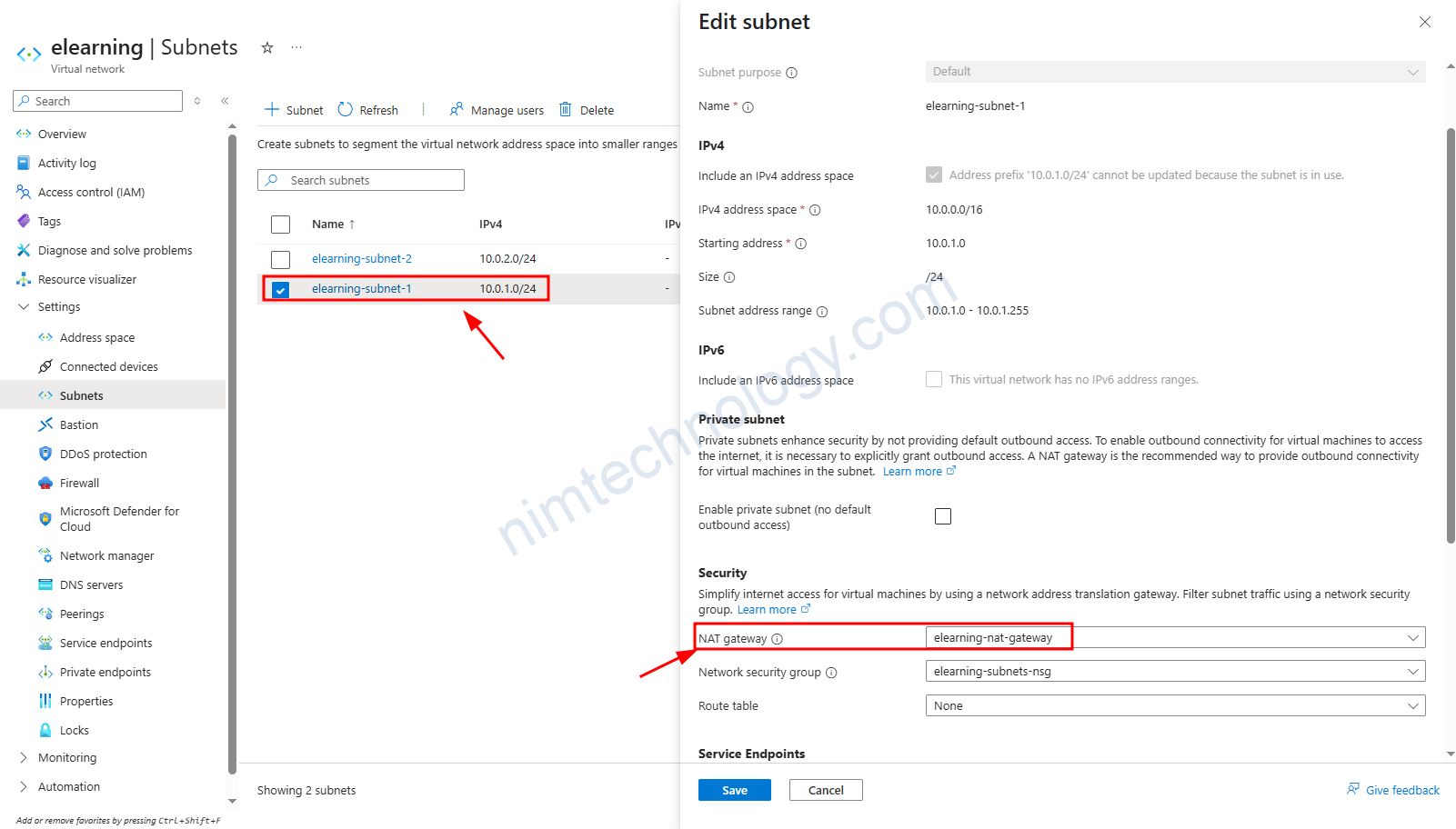
Sau khi khai bao variable sunet=[“10.0.1.0/24″,”10.0.2.0/24”] thì chúng ta đã có 1 subnet. được gắn vào vnet.
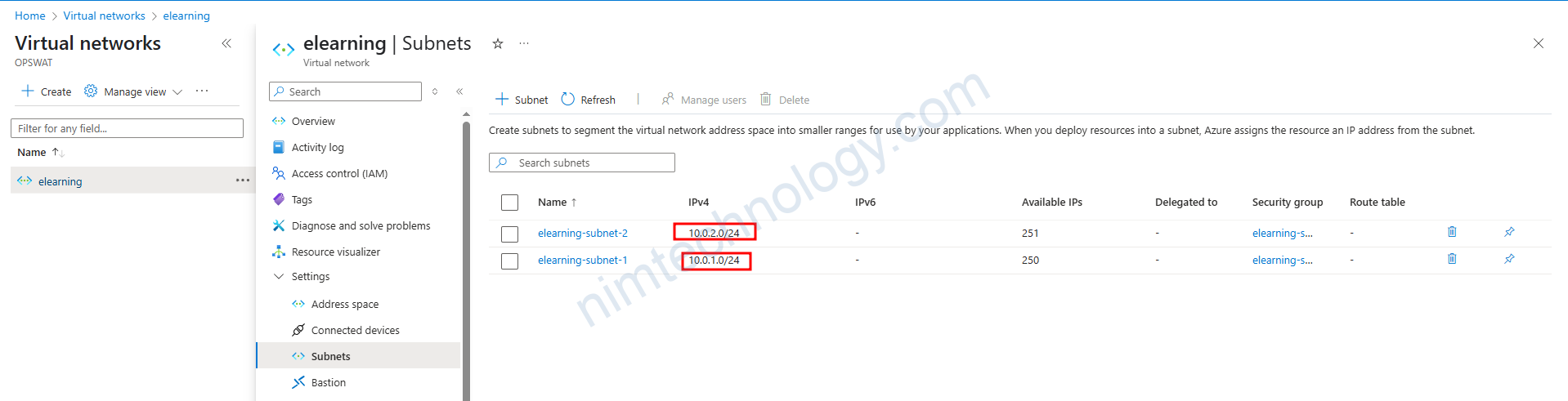
Chúng ta cũng vào tìm hiểu chỉ tiếp của Subnet này.
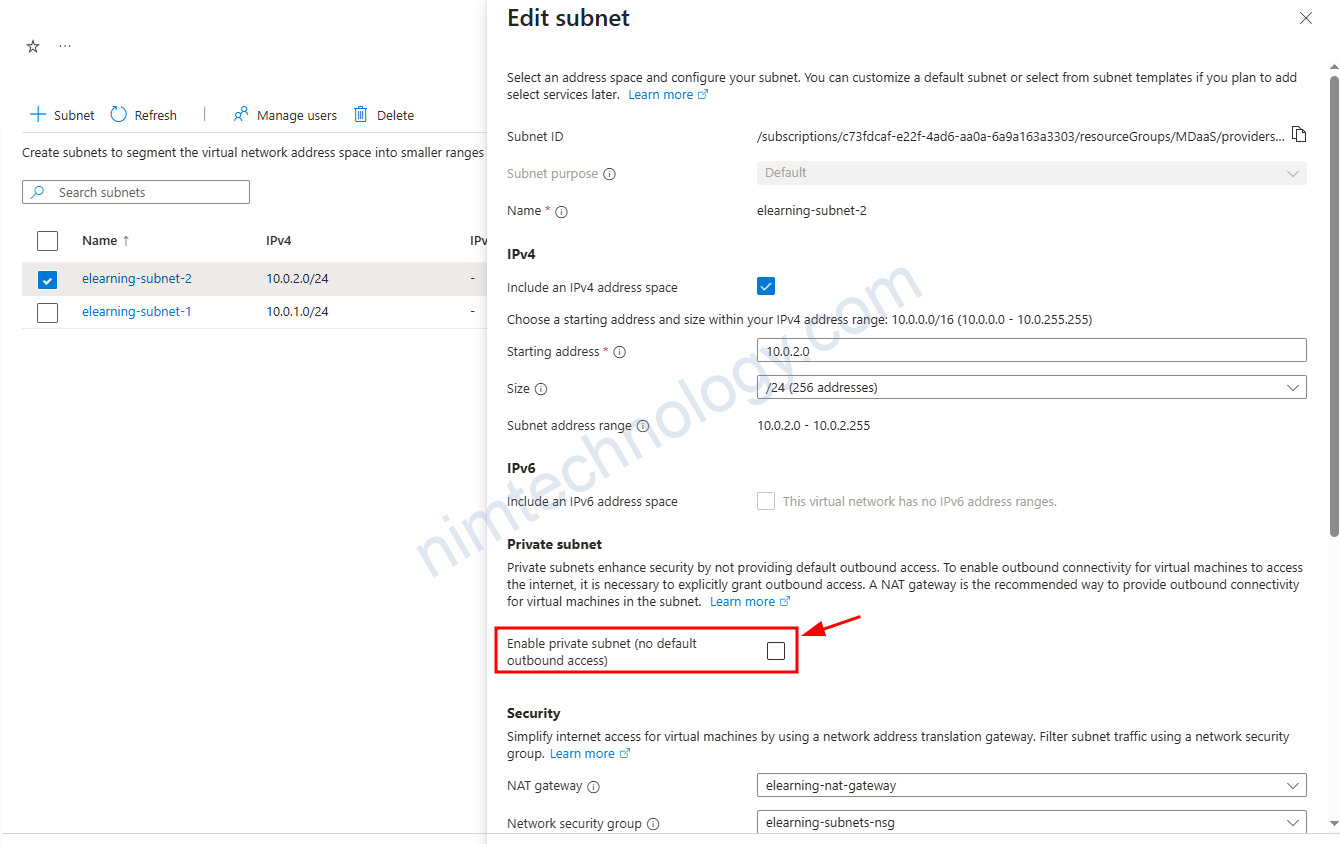
Trong subnet chúng ta có thể gắn được Nat Gateway để cho phép các VM trong subnet có thể đi ra internet theo được Nat Gateway
Network Security Group cũng giống như ACL của AWS nhưng nó apply cho Subnet.
Chúng ta cũng nhau tìm hiểu Enable private Subnet là gì?
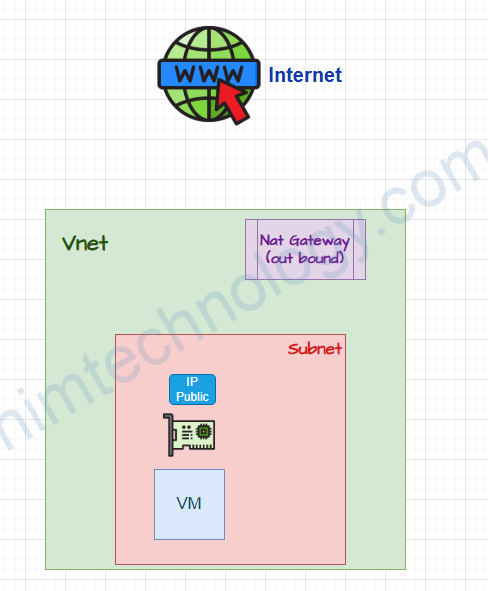
VM is attached IP Public and NAT Gateway is attached Subnet.
Lúc này hệ thống của chúng ta đã gắn NatGateway vào Subnet và VM đã được gắn IP public.
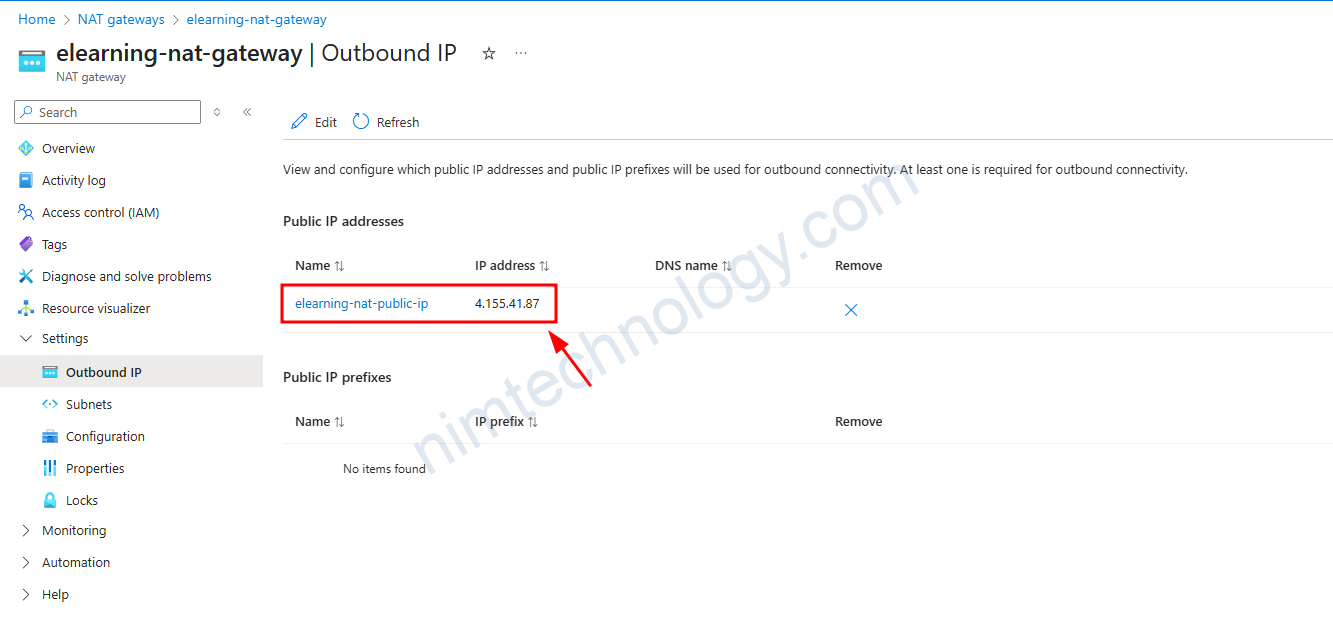
Bạn cũng có thể thấy giờ NAT có IP public là 4.155.41.87
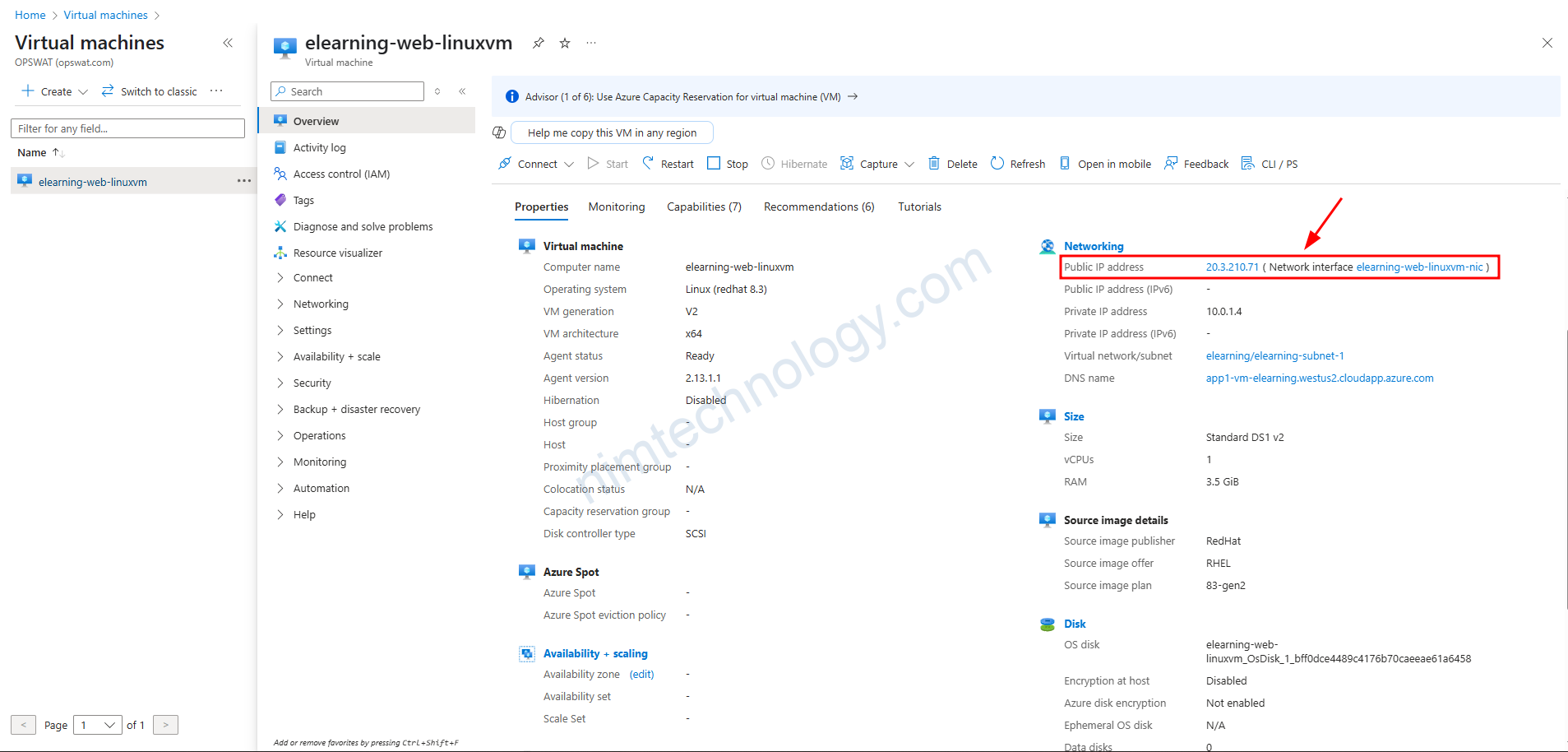
Với VM thì bạn thấy là nó đã được gắn với IP public là: 20.3.210.71 ( Network interface elearning-web-linuxvm-nic )
Case 1.1: Don’t set “Enable private subnet (no default outbound access)”
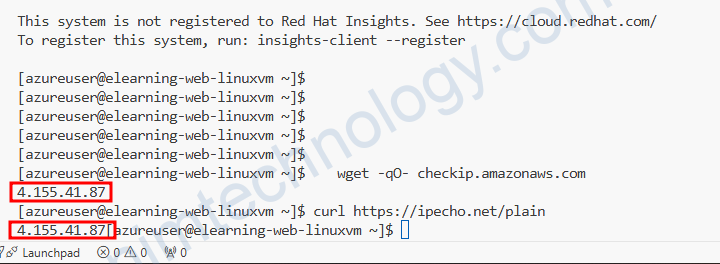
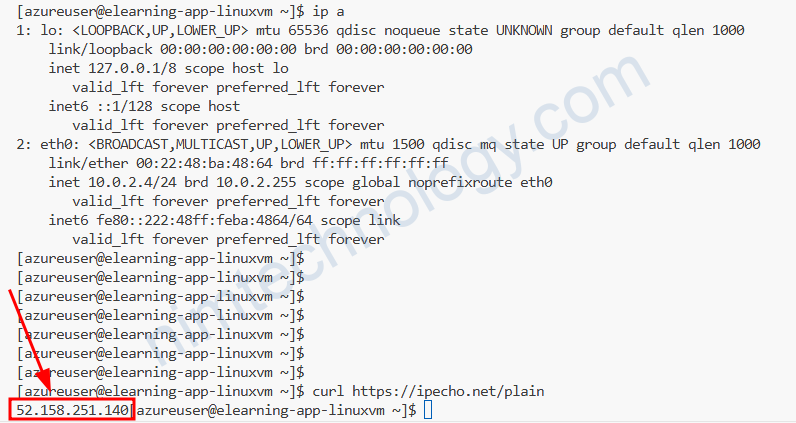
Chúng ta sẽ dùng các command sau để xác định chúng ta đang đi đường nào ra:
curl https://ipecho.net/plain wget -qO- checkip.amazonaws.com
Hiện tại đều là IP của NAT Gateway.
Case 1.2: Don’t set “Enable private subnet (no default outbound access)” and Nat Option is none.
Lúc này mình sẽ cho NAT Option trong subnet là None
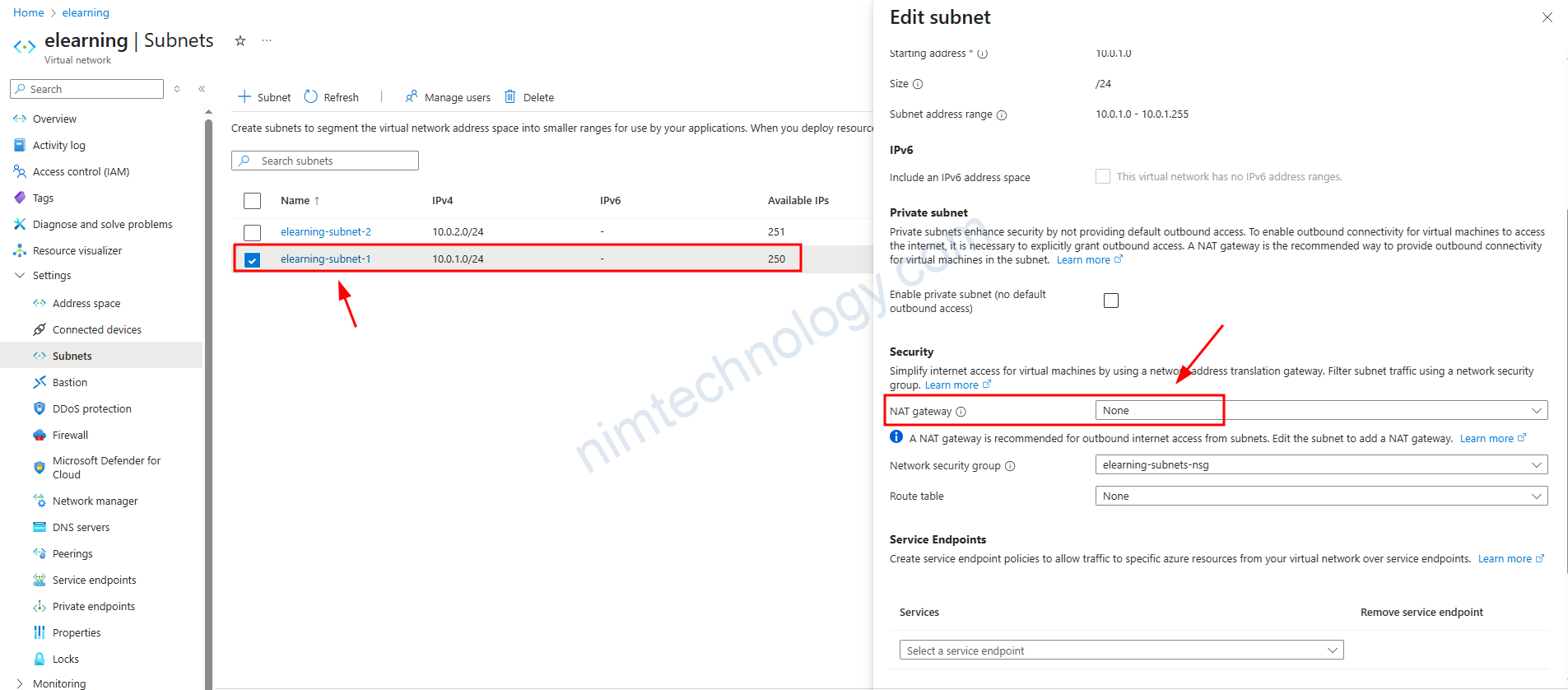
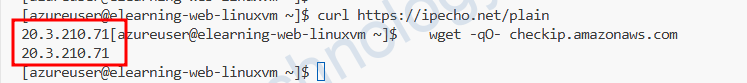
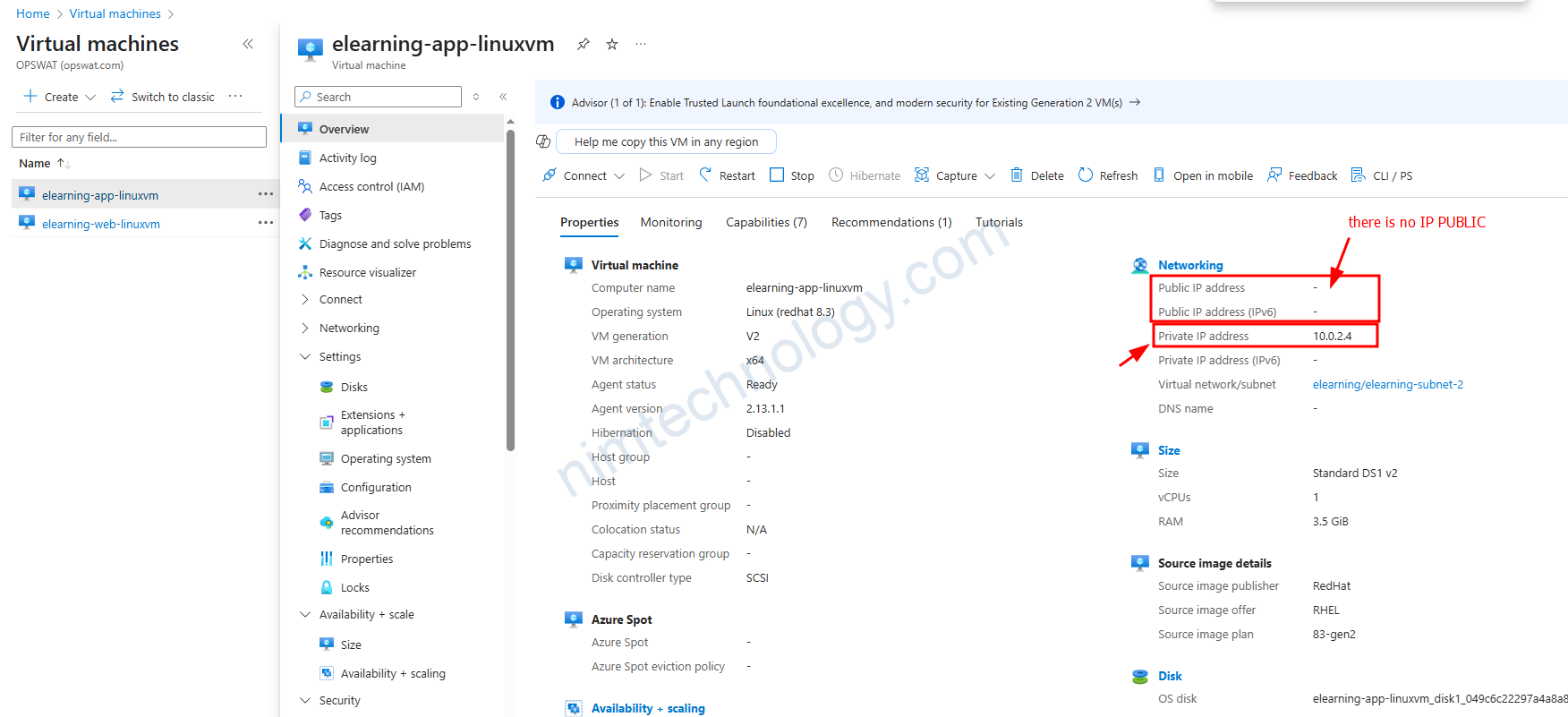
Lúc này IP public trả về là của IP được gắn trên Interface.
Case 1.2: Set “Enable private subnet (no default outbound access)” and Nat Option is none.
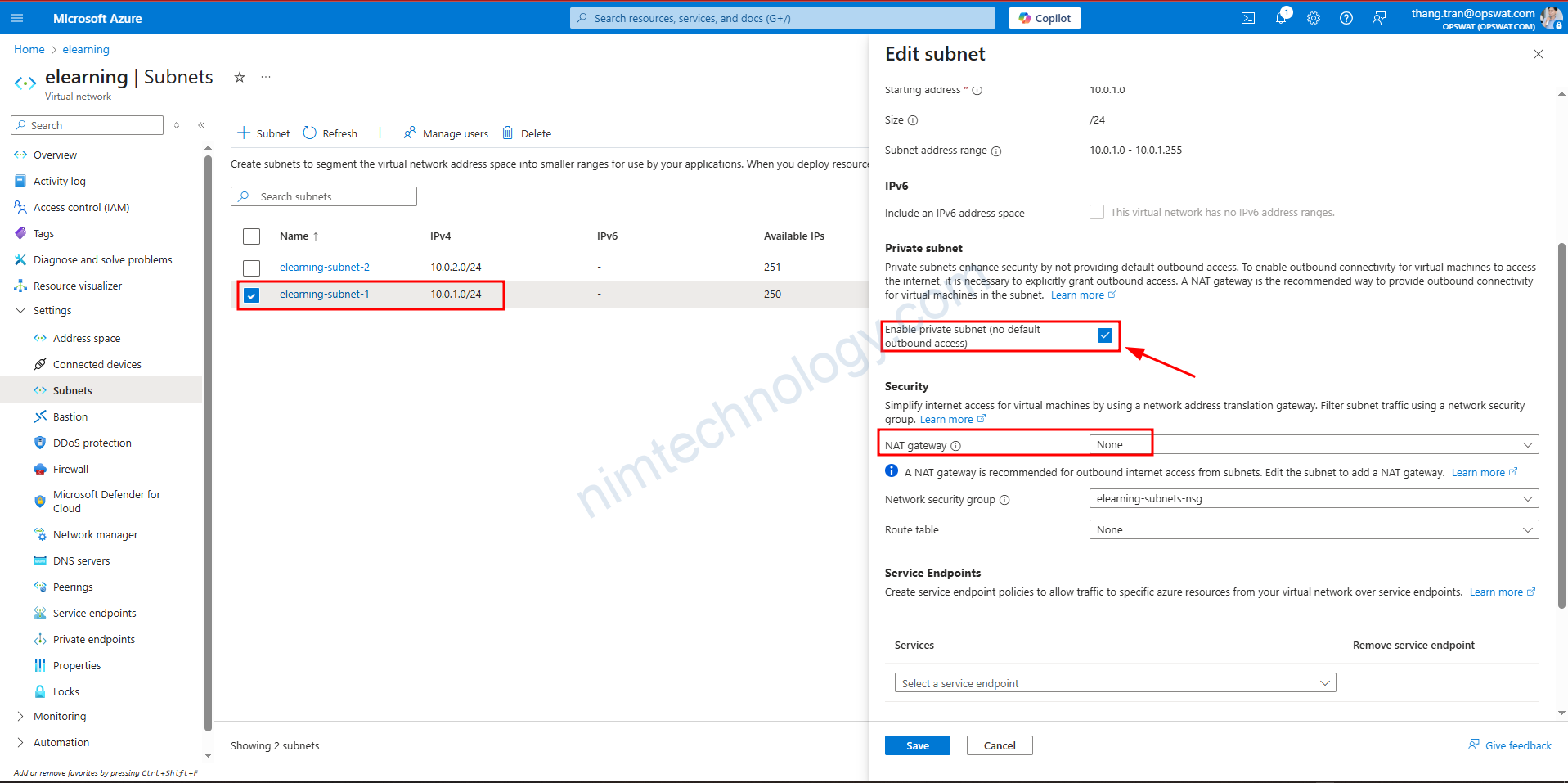
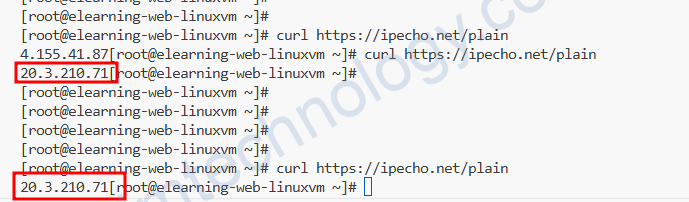
lúc này IP Public của VM là IP gắn trên interface của VM.
Case 1.3: Set “Enable private subnet (no default outbound access)” and Public IP is attached to VM, and the NAT Gateway is attached to the subnet.
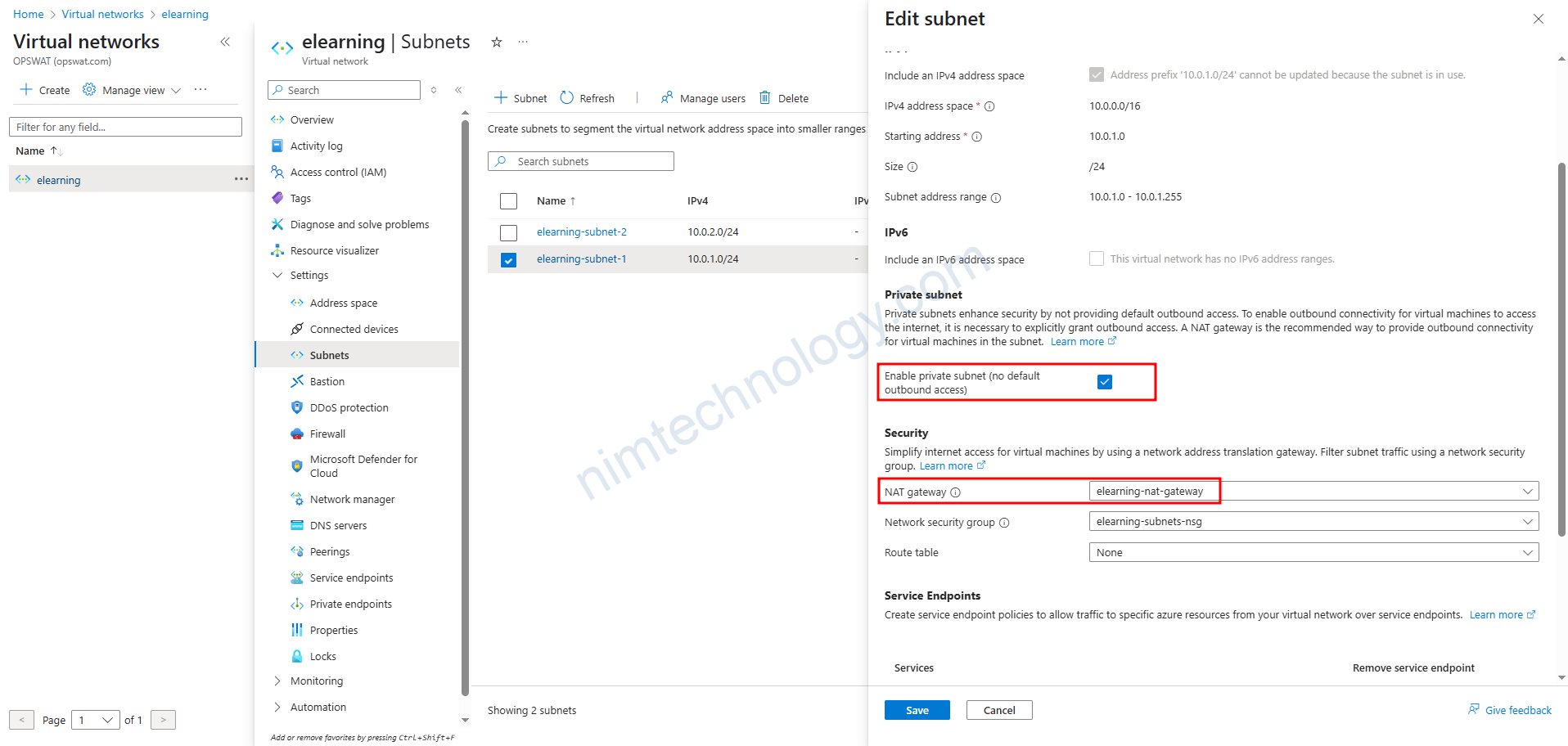
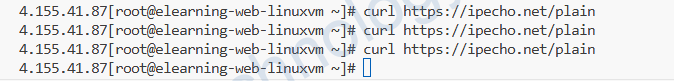
Vậy rốt cuộc Enable private subnet (no default outbound access) là gì?
Chúng ta sẽ cần đọc tài liệu này 1 chút:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/ip-services/default-outbound-access
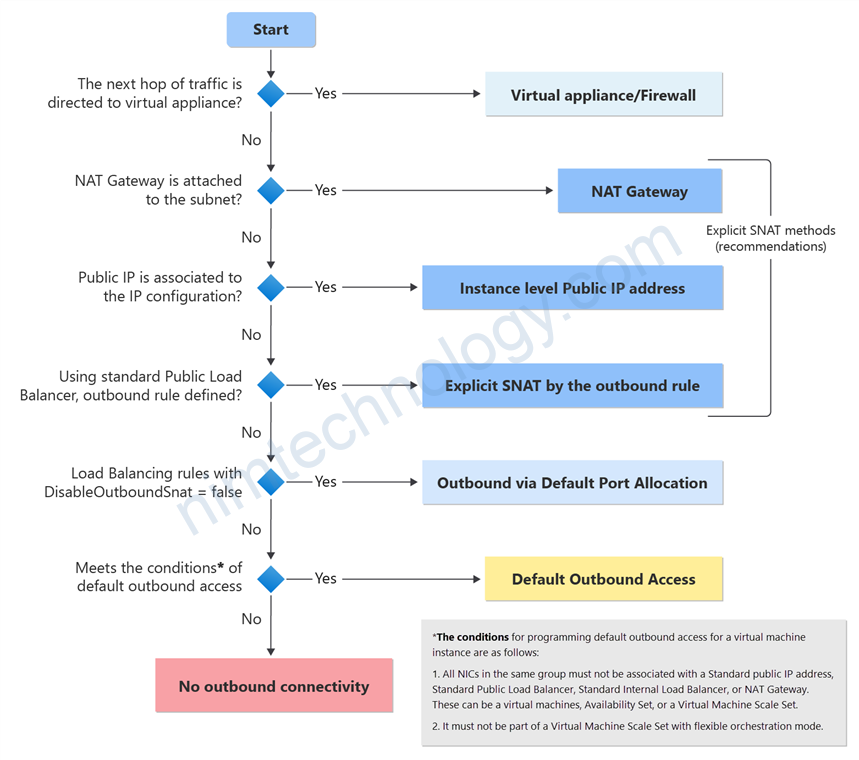
Bạn có thể thấy là khi một VM được tạo ra thì luôn được cung cấp 1 outbound mặc định để truy cập Internet.
Nghĩa là VM của bạn sẽ không cần IP Public và NAT nhưng vẫn ra được Internet.
Mình sẽ kiểm tra điều này:
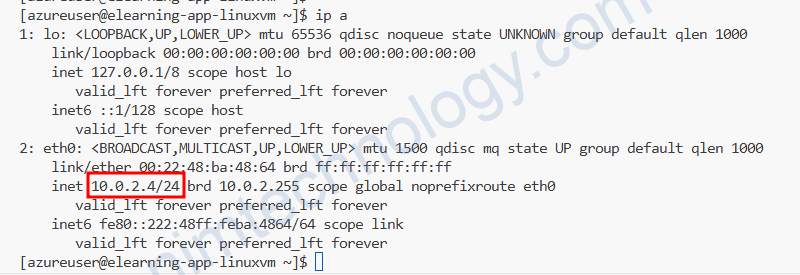
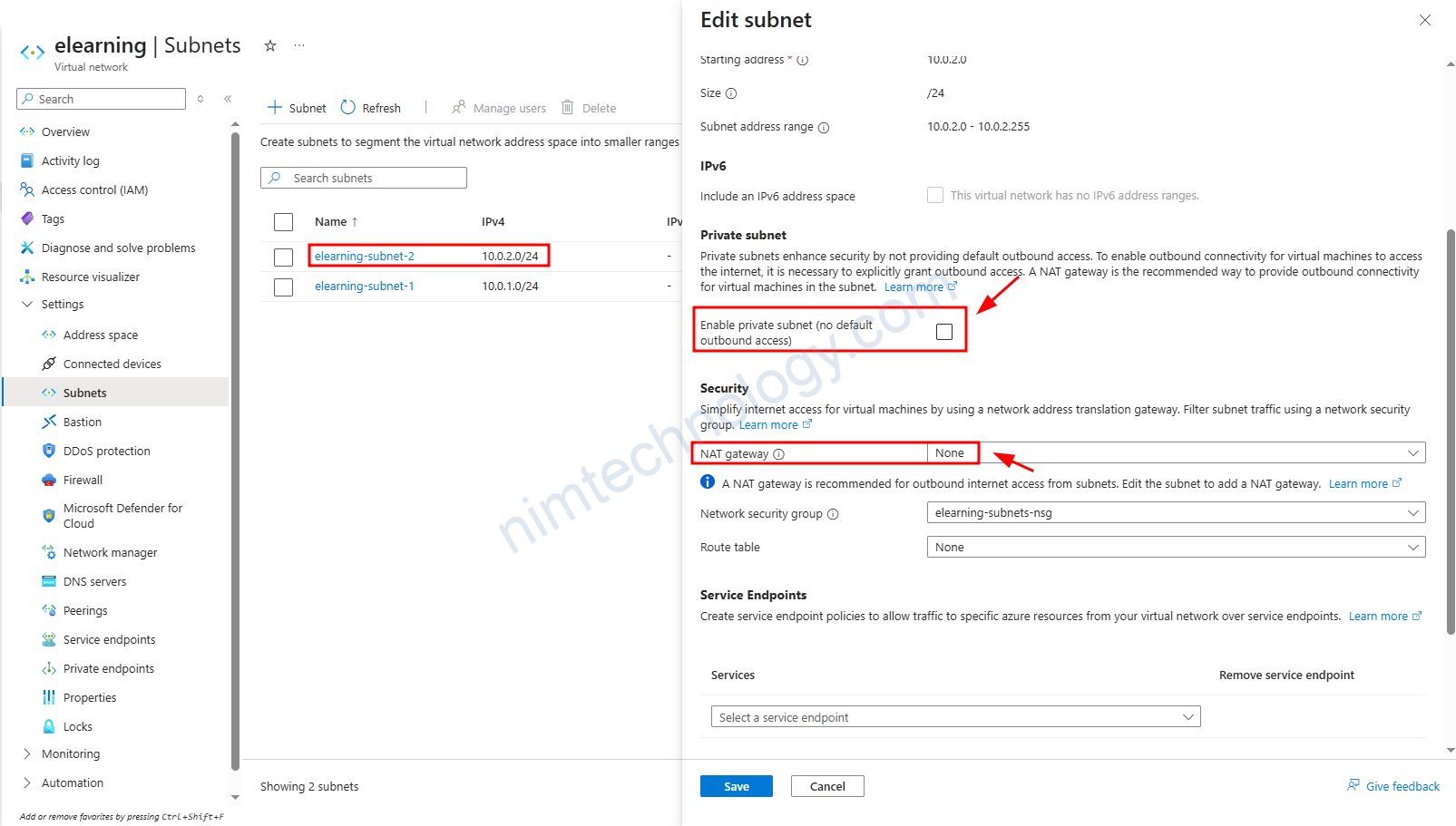
Bạn có thể thấy rằng mình đang không gắn NAT vào subnet. Nên VM sẽ không thể đi Internet bằng Nat Gateway.
Bây giờ nếu anh em tíc vào Enable private subnet (no default outbound access)
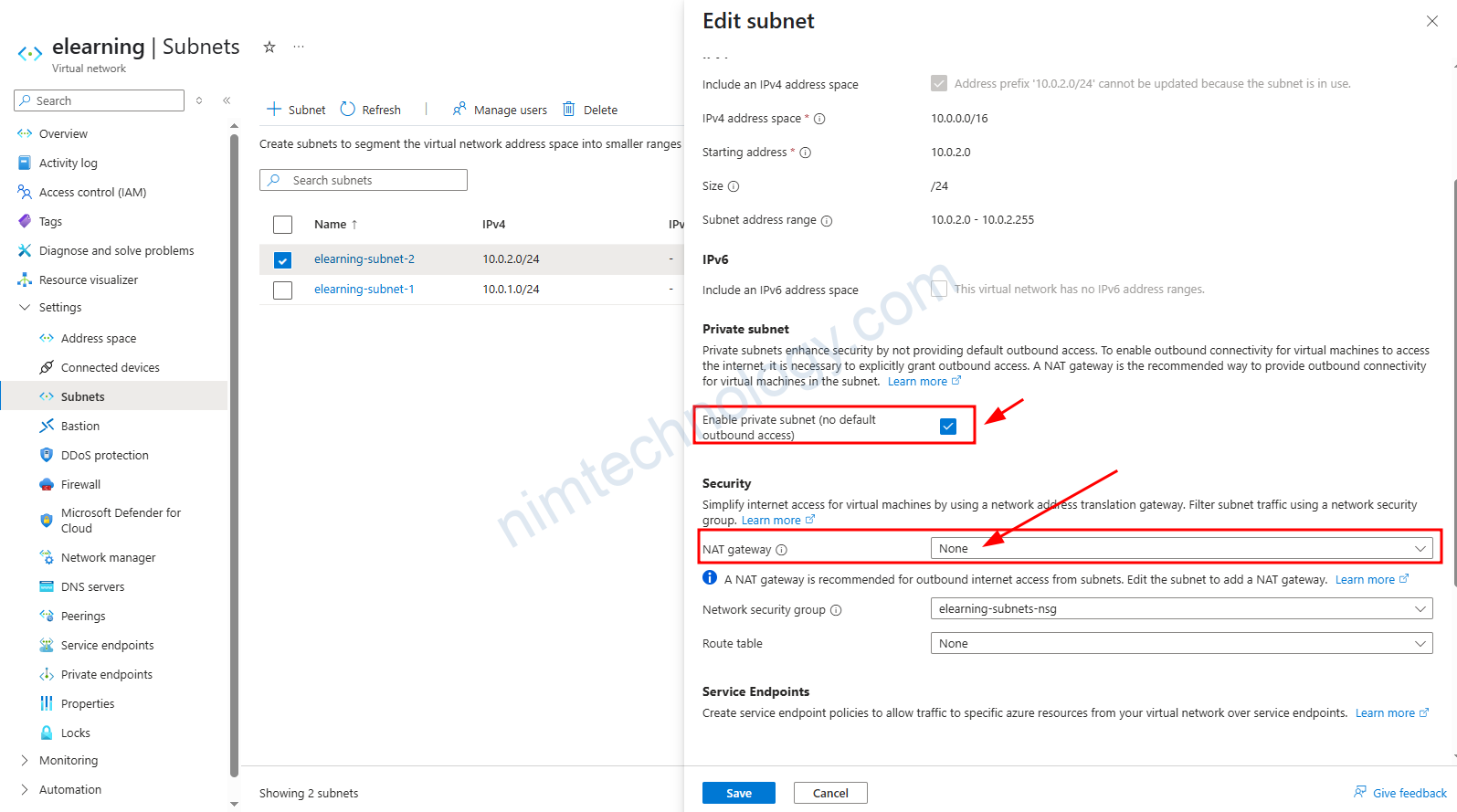
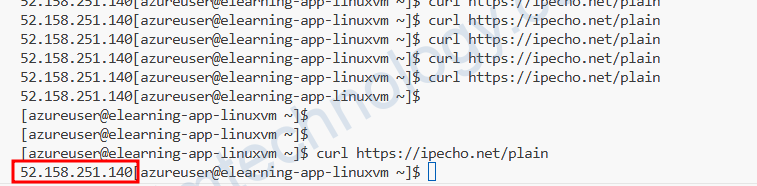
Hiện tại thì thấy tính năng cũng chưa hiệu quả gì.
Gần như nó không ngắt Connect internet default của Azure
Chúng ta có 1 thông báo vô cùng quan trọng.
Microsoft have announced that on the 30th of September 2025, they will be retiring default outbound connectivity for VMs. This means that any VMs deployed after this date will not have connectivity to the internet and if you need this, you will need to explicitly configure it. It is recommended that before this date you configure your resources to have connectivity if required. So let’s take a look at how that can be done.
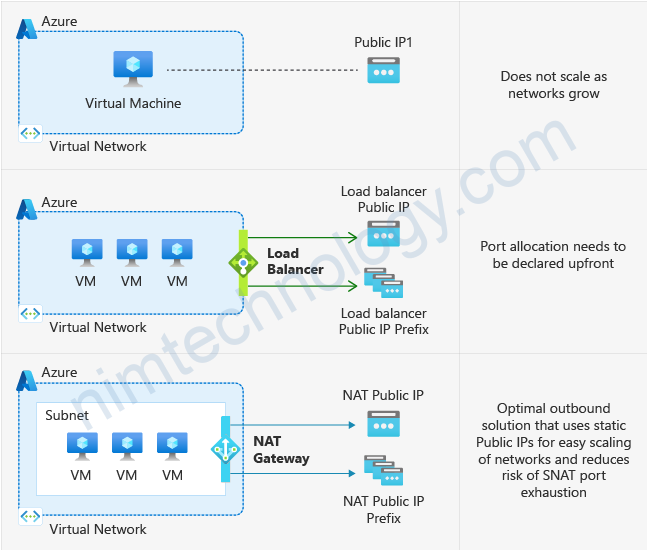
https://samcogan.com/retiring-default-internet-access-for-vms
3.4) Create Network Security for Subnet
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "subnets_nsg" {
name = "${var.vnet_name}-subnets-nsg"
location = var.resource_group_location
resource_group_name = var.resource_group_name
}
resource "azurerm_network_security_rule" "subnets_nsg_rule_inbound" {
for_each = var.inbound_ports_map
name = "Allow-Port-${each.value}"
priority = tonumber(each.key)
direction = "Inbound"
access = "Allow"
protocol = "Tcp"
source_port_range = "*"
destination_port_range = each.value
source_address_prefix = "*"
destination_address_prefix = "*"
resource_group_name = var.resource_group_name
network_security_group_name = azurerm_network_security_group.subnets_nsg.name
}
resource "azurerm_subnet_network_security_group_association" "subnets_nsg_assoc" {
depends_on = [azurerm_network_security_rule.subnets_nsg_rule_inbound]
count = length(azurerm_subnet.subnets)
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].id
network_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.subnets_nsg.id
}
Mặc định thì Network security Group sẽ chặn all và bạn cần rule gì thì bạn mở thì bạn tạo rule để allow.
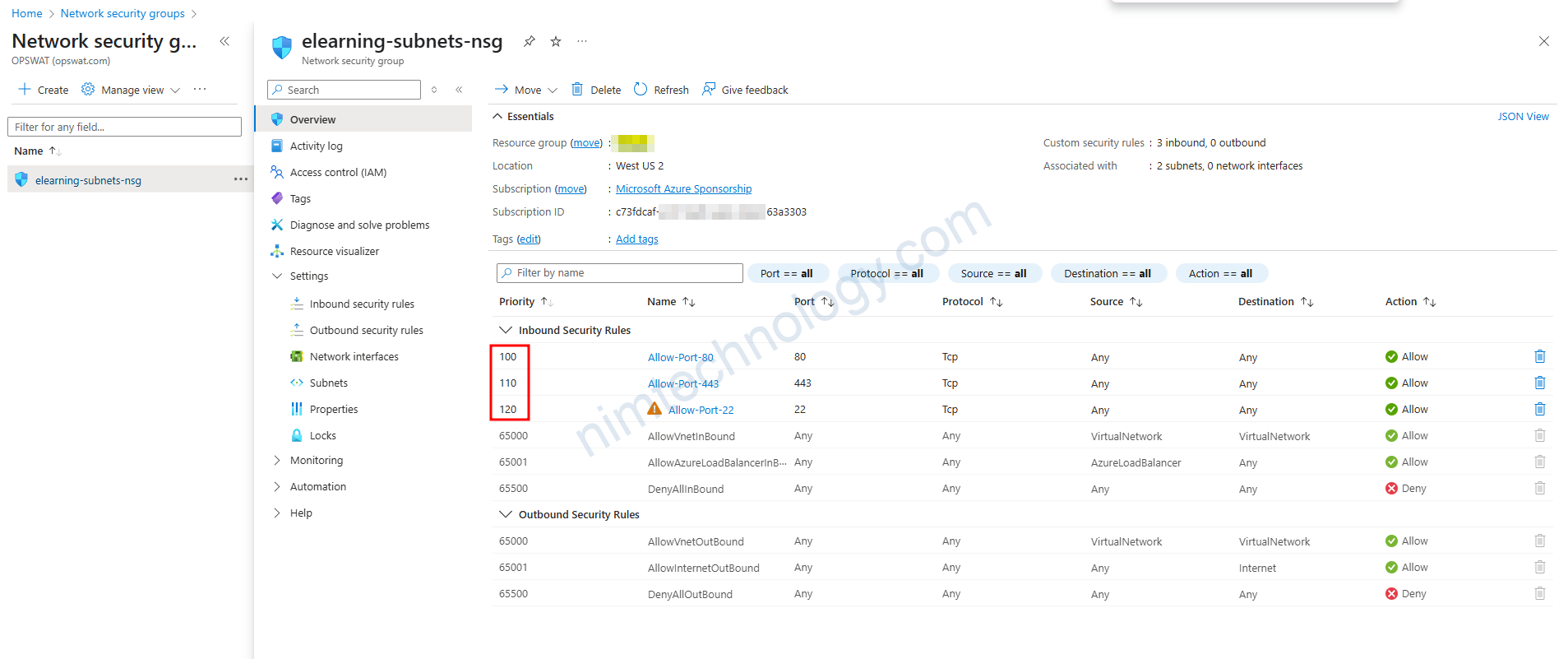
Có 1 điểm khác biết là ở đây các rule sẽ priority, số càng nhỏ thì độ ưu tiên càng cao.
3.5) route tables.
Có 1 điều khá đặc biệt là ở chúng ta không cần define 1 default route 0.0.0.0 đến Nat Gateway.
Nhưng VM trong Subnet vấn có thể đi đúng ra IP public hoặc NatGate way.
Và đây là chế độ Ưu tiên mà mình test được:
Nat Gateway > IP public > Default NatGateway of Azure.
Why Your VM Has Internet Access Without a Route Table?
By default, Azure provides each subnet with a system-generated route table that includes a route for internet-bound traffic:
- 0.0.0.0/0 → Internet: This route directs all traffic destined for addresses outside the virtual network to the internet. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-networks-udr-overview
What Happens If You Attach a Route Table?
When you associate a custom route table with a subnet, Azure combines the routes from the custom table with the default system routes. If your custom route table includes a route for 0.0.0.0/0 with a next hop type of None, it will override the default internet route, potentially blocking internet access.
Refer to:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61491978/how-to-see-azure-system-default-routes
Nếu có vấn để về route table đã affact lên VM như thể nào?
thì bạn sẽ cần check Effective Route
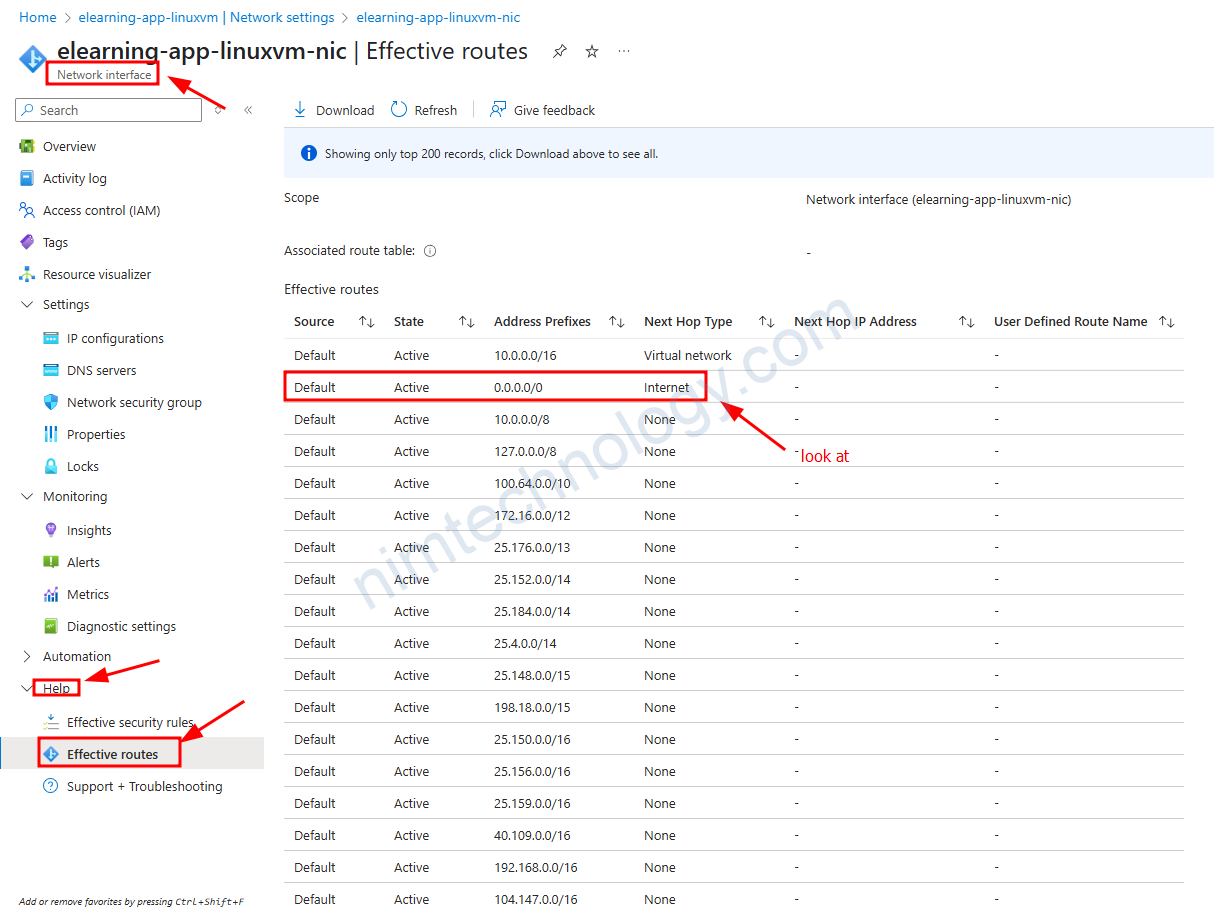
resource "azurerm_route_table" "route_table" {
for_each = length(var.routes) > 0 ? { "route_table" = "route_table" } : {}
name = "${var.vnet_name}-route-table"
location = var.resource_group_location
resource_group_name = var.resource_group_name
tags = local.merged_tags
}
resource "azurerm_route" "routes" {
for_each = var.routes
name = each.key
resource_group_name = var.resource_group_name
route_table_name = azurerm_route_table.route_table["route_table"].name
address_prefix = each.value.address_prefix
next_hop_type = each.value.next_hop_type
next_hop_in_ip_address = each.value.next_hop_in_ip_address
}
resource "azurerm_subnet_route_table_association" "subnet_route_assoc" {
count = length(var.routes) > 0 ? length(azurerm_subnet.subnets) : 0
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnets[count.index].id
route_table_id = azurerm_route_table.route_table["route_table"].id
}